The classic Groovy programming language for iPad, iPhone and iPod touch. Programming language is a perfect tool for studying, complex mathematical calculation, entertainment and many other useful tasks. The application is especially useful for learning the Groovy programming language. You have to buy compilations inside the application. Internet connection is required.
- You have to buy compilations inside the application.
- Internet connection is required.
Feedback
- The great programming tool on the AppStore.
- Your programming language for iOS is amazing!
Features
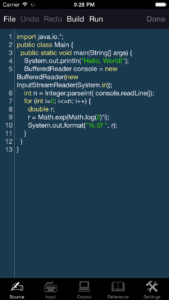
- Compile and run your program.
- Text input before program run and text output.
- Enhanced source code editor with syntax highlighting, line numbers, color themes and additional keyboard.
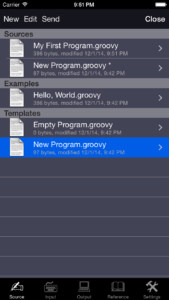
- Import and export programs by iTunes or by email.
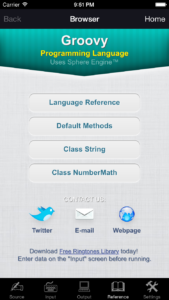
- Online language reference and several program samples.
Limitations
- Internet connection is required to compile and run a program.
- Graphics, network, file system and real-time input are not supported.
- Maximum running time of a program is 15 seconds.
- Use several classes on one source file instead separated files.
Thanks for using the application!
App Store
Supported languages: English.
Supported devices: iPhone, iPad and iPod.
Click on the icon to install:
See also: Java Programming Language.
Groovy is an object-oriented programming language for the Java platform. It is a dynamic language with features similar to those of Python, Ruby, Perl, and Smalltalk. It can be used as a scripting language for the Java Platform.
Groovy uses a Java-like bracket syntax. It is dynamically compiled to Java Virtual Machine (JVM) bytecode and interoperates with other Java code and libraries. Most Java code is also syntactically valid Groovy.
Groovy 1.0 was released on January 2, 2007.
James Strachan first talked about the development of Groovy in his blog in August 2003. Several versions were released between 2004 and 2006. After the JCP standardization process began, the version numbering was changed and a version called “1.0” was released on January 2, 2007. After various betas and release candidates numbered 1.1, on December 7, 2007, Groovy 1.1 Final was released and immediately rebranded as Groovy 1.5 as a reflection of the many changes that were made.
In July 2009, Strachan wrote on his blog that “I can honestly say if someone had shown me the Programming in Scala book by Martin Odersky, Lex Spoon & Bill Venners back in 2003 I’d probably have never created Groovy.” Strachan left the project silently a year before the Groovy 1.0 release in 2007.
Many (but not all) valid Java files are also valid Groovy files. Although the two languages are similar, Groovy code can be more compact, because it does not require all the elements that Java requires. This makes it possible for Java programmers to gradually learn Groovy by starting with familiar Java syntax before acquiring more Groovy idioms.
Groovy features not available in Java include both static and dynamic typing (with the def keyword), closures, operator overloading, native syntax for lists and associative arrays (maps), native support for regular expressions, polymorphic iteration, expressions embedded inside strings, additional helper methods, and the safe navigation operator “?.” to automatically check for nulls (for example, “variable?.method()”, or “variable?.field”).